Chronic prostatitis is a serious problem. Even modern urology is not able to answer many questions about this pathology. Experts believe that chronic prostatitis is a disease that is the result of a whole host of health problems, which include tissue damage as well as dysfunctions not only of the urinary tract and prostate, but also of other organs.
The pathology is diagnosed mainly in men of reproductive age. In older men, chronic prostatitis is often accompanied by benign prostate cancer.
Disease classification
The classification of prostatitis was developed by scientists at the US National Institutes of Health in 1995:
%20and%20chronic%20inflamed%20prostatitis%20(right).webp)
- 1 type- acute bacterial prostatitis. It is diagnosed in 5% of cases of prostate inflammation.
- type 2- chronic bacterial prostatitis.
- 3 type- chronic bacterial prostatitis. This pathology has another name - chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
- type 3A- an inflammatory form of chronic prostatitis. It is diagnosed in 60% of cases of chronic prostatitis.
- type 3B- non-inflammatory form of chronic prostatitis. Diagnosed in 30% of cases.
- 4 type- asymptomatic prostatitis.
There is also a classification of chronic prostatitis, compiled in 1990.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis
Feeling of discomfort and pain in the pelvic region that lasts for more than 3 months are the main symptoms of chronic prostatitis.
In addition, urinary disorders and erectile dysfunction are observed:
- pain occurs in the perineum, it can radiate to the anus, groin, inner thigh, sacrum, lower back and scrotum. Pain, on the one hand, that extends to the testicle is often not a symptom of chronic prostatitis;
- erection does not occur despite the presence of suitable conditions, but complete impotence is not observed;
- in the early stages of the development of the disease, premature ejaculation is observed;
- frequent urination, urinary incontinence, pain and burning sensation in the process of emptying the bladder.
The clinical picture may differ depending on the type of chronic prostatitis.
infectious form:
- frequent urination at night;
- pain in thighs, perineum, glans and rectum, aggravated by movement;
- pain when urinating;
- weak stream of urine.
Specific infectious:
- mucous discharge from the urethra;
- the above symptoms.
Non-infectious prostatitis:
- sharp pain in the perineum;
- pain in the thighs and head of the penis;
- the pain intensifies with the forced interruption of sexual intercourse or the prolonged absence of intimate life.
Important!The disease progresses in waves. Symptoms may weaken or intensify, but their presence clearly indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
Symptoms may vary depending on the stage of development of the pathology.

The following stages of development of the pathology are distinguished:
- exudative.The patient feels pain in the pubis, groin and scrotum. There is frequent urination and a feeling of discomfort after intercourse. An erection can hurt.
- Alternative.The pain intensifies, is located in the groin, pubic part and gives to the sacrum. Urination is accelerated but occurs without difficulty. Erection does not suffer.
- proliferative.During an exacerbation, urination becomes more frequent. Urine flow becomes weak.
- scar.Sclerosis of prostate tissue occurs. There is a feeling of heaviness in the sacrum and pubic region. Increased urination. Erection becomes weak. Ejaculation may be completely absent.
Symptoms may vary depending on the course of the disease, but in any case, they will gradually increase.
Causes of chronic prostatitis
There are many factors that lead to chronic prostatitis. The disease occurs under the influence of infectious agents. The patient has hormonal, neurovegetative, immunological and hemodynamic disorders. Biochemical factors, reflux of urine into the lobes of the prostate and impaired functioning of growth factors, which are responsible for the proliferation of living cells, affect.
Reasons that affect the formation of pathology:
- infections of the genitourinary system;
- hypodynamia;
- irregular sex life;
- continuous bladder catheterization;
- regular hypothermia.
Developmentbacterial diseasespromotes intraprostatic urinary reflux.
Chronic abacterial prostatitisdevelops against the background of neurogenic disorders of the pelvic floor muscles, as well as elements responsible for the functioning of the bladder wall, prostate and urethra.
Trainingmyofascial trigger points, which are located near the organs of the genitourinary system and the prostate, can cause pelvic pain syndrome. Stitches resulting from certain diseases, surgical interventions and injuries can cause pain in the pubic region, perineum and adjacent areas.
pathology diagnosis
The presence of a symptom complex makes it possible to diagnose chronic prostatitis without much difficulty. However, in some cases, the pathology can be asymptomatic. In this case, in addition to the standard examination and patient questioning, additional research methods are needed.A neurological examination and study of the patient's immune status are mandatory..
Important!Special questionnaires and questionnaires allow you to more accurately determine the patient's subjective feelings and get a complete picture of their health status, pain intensity, ejaculation, erection and urination disorders.
laboratory diagnosis
Laboratory diagnosis makes it possible to distinguish between a bacterial and abacterial form of pathology, as well as to determine the type of pathogen and make the diagnosis more accurate.Chronic inflammation of the prostate is confirmed when the fourth urine sample or prostate secretion contains more than 10 leukocytes in the PZ, or bacterial associations.When the number of leukocytes is increased but bacteria are not seeded, the material is examined for chlamydia or other STD pathogens.
- The discharge from the urethra is sent to the laboratory to detect viral, fungal and bacterial flora, leukocytes and mucus in it.
- The urethral scraping is examined by PCR. This makes it possible to identify pathological agents that are sexually transmitted.
- Perform a microscopic examination of the prostate secretion to count the number of macrophages, leukocytes, amyloid and Trousseau-Lallemand bodies. An immunological study and a bacteriological study are prescribed. Determine the level of non-specific antibodies.
- Blood sampling is performed ten days after a digital rectal exam to determine the concentration of PSA in it. At a rate above 4. 0 ng/ml, the patient undergoes a prostate biopsy to rule out oncology.
The diagnosis is displayed on the basis of results of researches.
Instrumental diagnostics

To clarify the stage and form of the disease will help transrectal ultrasound of the gland. Ultrasound makes it possible to exclude other diagnoses, monitor the effectiveness of the treatment, in addition to determining the size of the prostate, its ecostructure, homogeneity and density of the seminal vesicles. Urodynamic studies and myography of the pelvic floor muscles will reveal bladder outlet obstruction and neurogenic disorders that often accompany the pathology.
CT and MRI are used to make a differential diagnosis, in particular, with prostate cancer. These methods will reveal violations in Organs pelvic organs and spine.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is important, as there is a risk of the patient having a more serious disease.
Differential diagnosis is established with such diseases:
- pseudodyssynergia, functional disorder of the detrusor-sphincter system, bladder dysfunction of neurogenic origin, complex regional pain syndrome;
- bladder stenosis, hypertrophic changes in the bladder neck, prostate adenoma;
- osteitis of the pubic joint, cystitis;
- rectal pathology.
If symptoms occur, the prostate should be examined by a urologist or andrologist.. Get an ultrasound. If necessary, a prostate biopsy is prescribed.
Pathology treatment methods
Chronic prostatitis is treated by a urologist or andrologist. Therapy is carried out in a complex way. Correction is subject to the patient's lifestyle, thinking characteristics and habits. It's important to move more, minimize alcohol consumption, kick nicotine addiction, eat right, and normalize your sex life. However, forgoing a course of basic therapy will not work. Taking medication is the main condition for a full recovery.
Indications for hospitalization
Most of the time, treatment is performed on an outpatient basis. But in cases where the disease cannot be corrected and tends to relapse, the patient is referred to a hospital where treatment is more effective.
medical method of treatment
This method aims to eliminate the existing infection, normalize blood circulation, improve the drainage of the prostate lobes, correct the hormonal background and immune status. Therefore, doctors prescribe antibiotics, vasodilators, immunomodulators, anticholinergics and anti-inflammatories.
If the pathology is bacterial in nature, antibiotics are definitely recommended. The agent is prescribed based on the results of bacterial culture of the prostate secretion.This will make it possible to isolate the pathogen with the subsequent determination of its sensitivity to a particular drug. With a well-designed scheme, the effectiveness of the treatment reaches more than 90%.
In the abacterial form, a short course of antibiotics is prescribed. It is continued only if the scheme gives a positive result. The effectiveness of therapy is approximately 40%
With chronic pelvic pain, the duration of the course of antibiotics is not more than one month. With positive dynamics, the treatment continues for another month. If there is no effect, the drug is replaced by another, which may be more effective.
Antibacterial agents from the fluoroquinolone group are the main drugs for the treatment of the pathology.They have high bioavailability, are active against most gram-negative bacteria, ureaplasmas and chlamydia, accumulate in prostate tissues.
When treatment with fluoroquinolones is not effective, penicillins may be prescribed.
Antibacterial drugs are used for preventive purposes.
After treatment with antibiotics, therapy with the use of a-blockers is prescribed.This treatment strategy is effective for patients who have persistent obstructive and irritative symptoms.
If urination disorders and pain persist, tricyclic antidepressants, which have an analgesic effect, may be prescribed.
With serious violations of urination, before starting therapy, a urodynamic study is carried out and acts on the basis of the results obtained.
non-drug therapy
Non-drug therapy methods allow you to increase the concentration of antibacterial drugs in the gland tissues, but exceeding the dose is not recommended.
For this, the following methods are used:
- electrophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- Phonophoresis;
- Microwave hyperthermia (applied transrectally).
When applying the last method, the temperature is selected individually. The temperature, set in the range of 39-40 degrees, allows you to increase the concentration of the drug in the body, activates the immune system at the cellular level, eliminates bacteria, relieves congestion. Increasing the range to 40-45 degrees allows for a sclerosing and analgesic effect.
Laser and magnetic therapy are used in combination. The effect is similar to the effect of the above methods, but it also has a biostimulating effect on the organ.
Transrectal massage is performed only in the absence of contraindications.
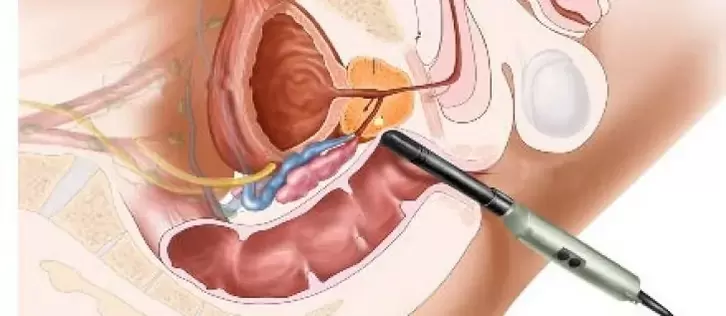
surgical method
Chronic prostatitis usually does not require surgery. The exception is complications that pose a threat to the patient's health and life. Modern surgical treatment allows the use of endoscopic surgery. It is minimally invasive. Rehabilitation is faster and minimal damage is done to the body.
The surgical method is prescribed for:
- prostate sclerosis;
- prostate adenoma;
- seed tuber sclerosis;
- calcification in the prostate.
Important!Surgery is contraindicated in the acute phase. Surgical treatment is prescribed by the surgeon based on the results of the study and the overall clinical picture.
Prognosis for chronic prostatitis
Doctors are cautious in predicting the outcome of the disease. It is rare to achieve complete recovery. Basically, chronic prostatitis enters a long-term remission stage. Symptoms disappear, urine and blood counts return to normal. So that chronic prostatitis does not become more active and does not cause complications, it is necessary to follow all the recommendations of a specialist.